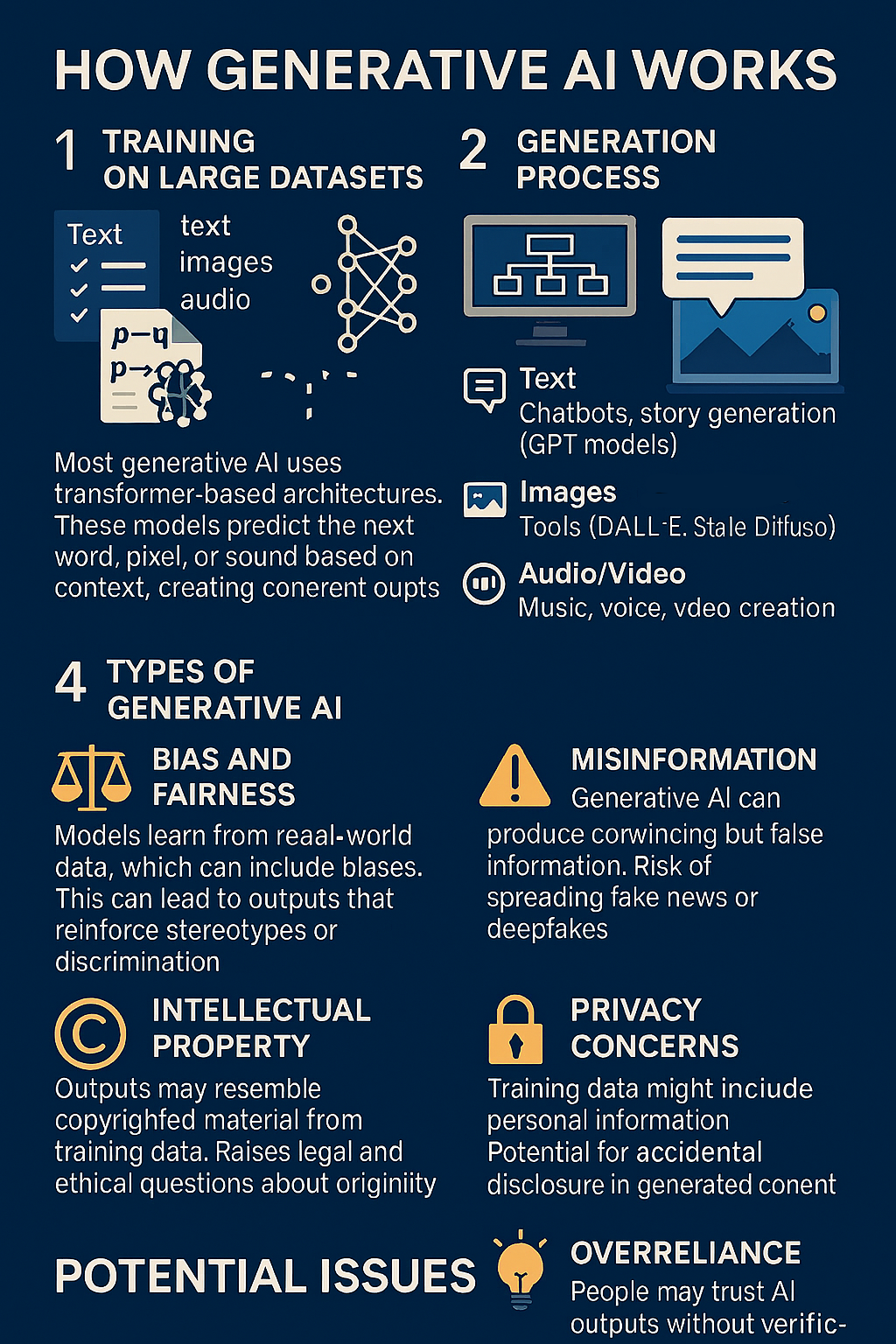
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to systems that can create new content—text, images, audio, or video—based on patterns learned from large datasets.
How It Works
- Training on Large Datasets
- Models are trained on billions of examples of text, images, or audio.
- They learn patterns, relationships, and structures using deep neural networks.
- Neural Network Architecture
- Most generative AI uses transformer-based architectures.
- These models predict the next word, pixel, or sound based on context.
- Generation Process
- When given a prompt, the model uses probabilities to generate new content.
- It doesn’t “think” or “understand”—it predicts what is likely to come next.
- Types of Generative AI
- Text: Chatbots, story generators (e.g., GPT models).
- Images: Tools like DALL·E or Stable Diffusion.
- Audio/Video: Music composition, voice synthesis, video creation.
Potential Issues
- Bias and Fairness
- Models learn from real-world data, which can include biases.
- Outputs may reinforce stereotypes or discrimination.
- Misinformation
- AI can produce convincing but false information.
- Risk of spreading fake news or deepfakes.
- Intellectual Property
- Outputs may resemble copyrighted material.
- Raises legal and ethical questions about originality.
- Privacy Concerns
- Training data might include personal information.
- Potential for accidental disclosure.
- Overreliance
- People may trust AI outputs without verification.
- Can reduce critical thinking and creativity.
The image below is an example of an infographic created using Generative AI. Note that, at first glance, it appears to meet the needs; however, upon closer inspection, you will notice numerous spelling mistakes and errors.
Key Takeaway
Generative AI is powerful for creating content, but it comes with ethical, legal, and social challenges that need careful management.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.